In this scenario, you send the changes from your local repository to Plesk, and then Plesk deploys the changes to your web site.
To create a new Git repository for your domain, go to Websites & Domains > Git. If you have already created Git repositories for your domain via Plesk, click the Add Repository button. You will see the screen for creating a new repository:
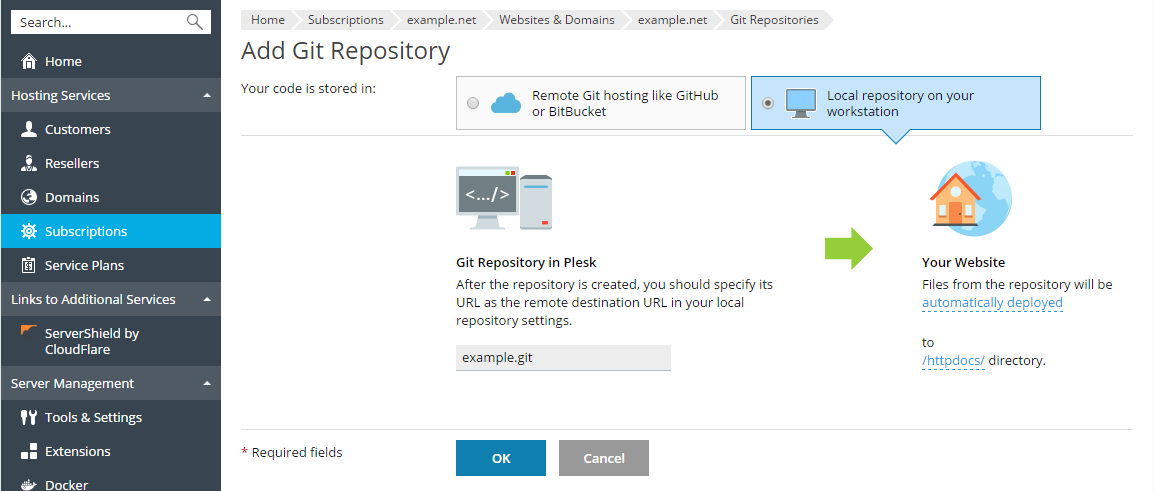
First, you have to select where your code is stored. In this scenario, select Local repository on your workstation.
Git Repository in Plesk. Specify the repository name. By default, the name of the domain is used with the .git suffix.
In the Your Website section, specify the following:
/httpdocs directory is used. You can change it to another existing directory by clicking the directory name.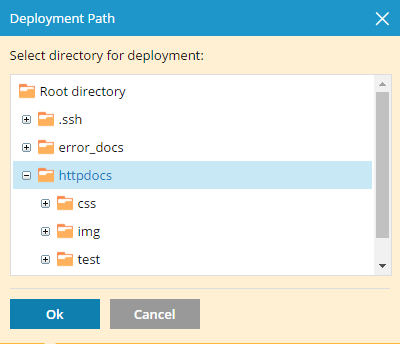
Click OK. The new repository will be created and displayed on the Git page.
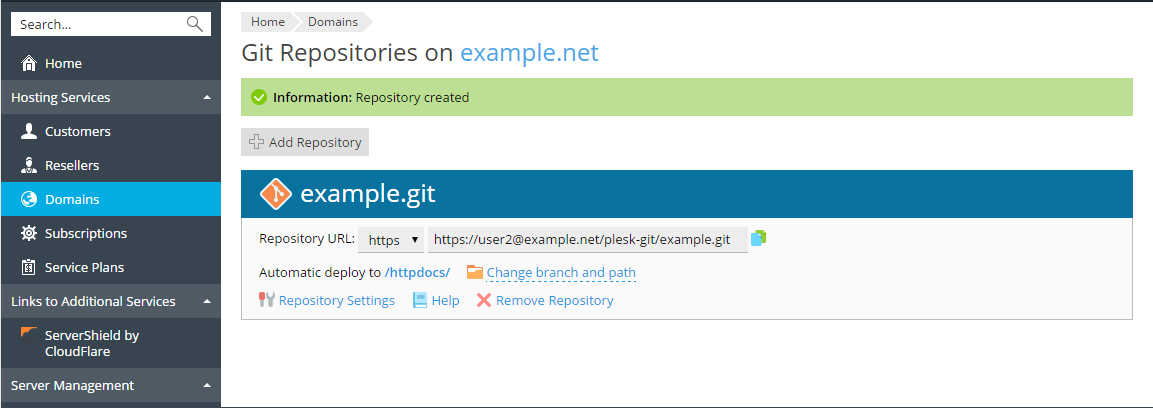
The displayed repository URL depends on the data transfer protocol that you use. You can select one of the following protocols:
Follow the instructions available from the Help link to initialize the local repository.
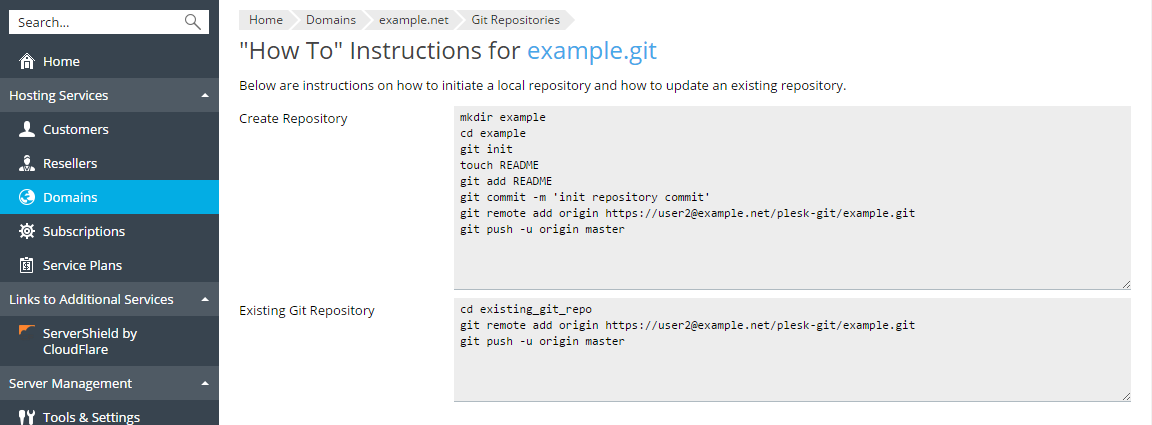
When the repository is initialized, you can see the commit information and the active branch name at Websites & Domains > Git. By default, the master branch is used to work with Plesk. You can add more branches later (see the Change Branch or Path section).
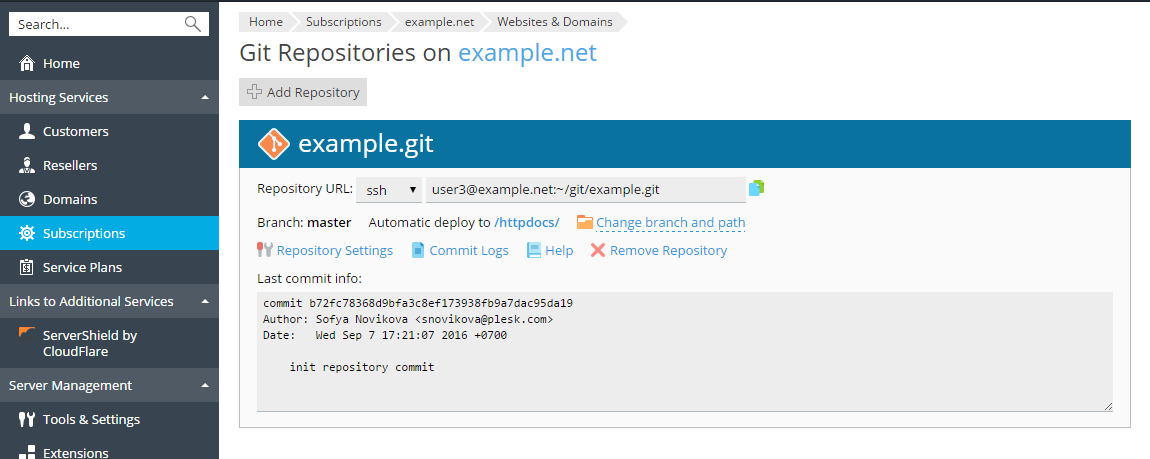
Now you can commit your web site files from your local repository and push them to the server repository.
When you commit your web site files from your local repository and push them to the server repository, you can see the commit information at Websites & Domains > Git.
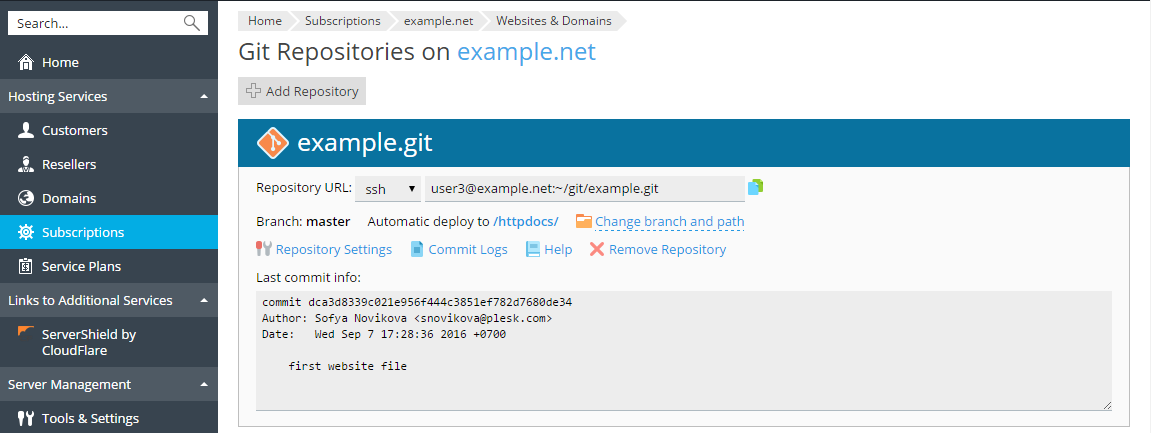
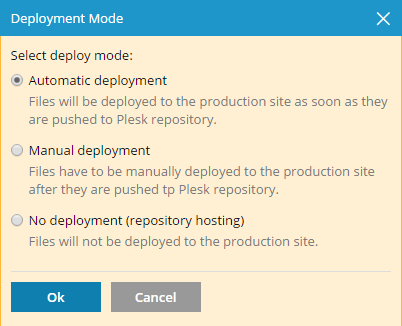
By default, Plesk uses the Automatic deployment mode. This means that after a file is pushed to the repository, it is immediately deployed to the target directory (you can switch off this mode if necessary, see the Select Deploy Mode section).
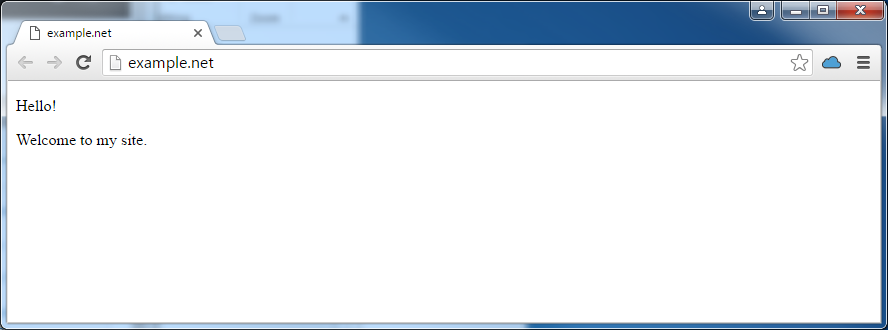
For example, if you commit and push an index.html file with the text “Hello! Welcome to my site.” to the Git repository, you can immediately click the web site URL to see the changes.
Deploy from a new branch
It is a normal practice to work with several branches in one repository. Only one branch can be active at one time. By default, the master branch is used for deployment.
To add one more branch, you have to create it in your local repository. For example, you can add the dev branch using the commands:
git branch dev
git checkout dev
Then commit the files to this branch and push to the server’s repository, using the commands:
git commit –m "changes to branch"
git push –u origin dev
Now you can select one of two active branches. Go to Websites & Domains > Git, click the Change branch and path link, and in the opened window select the branch name in the Branch menu.
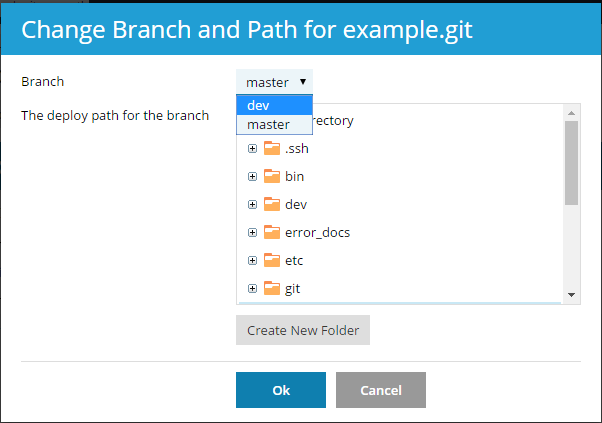
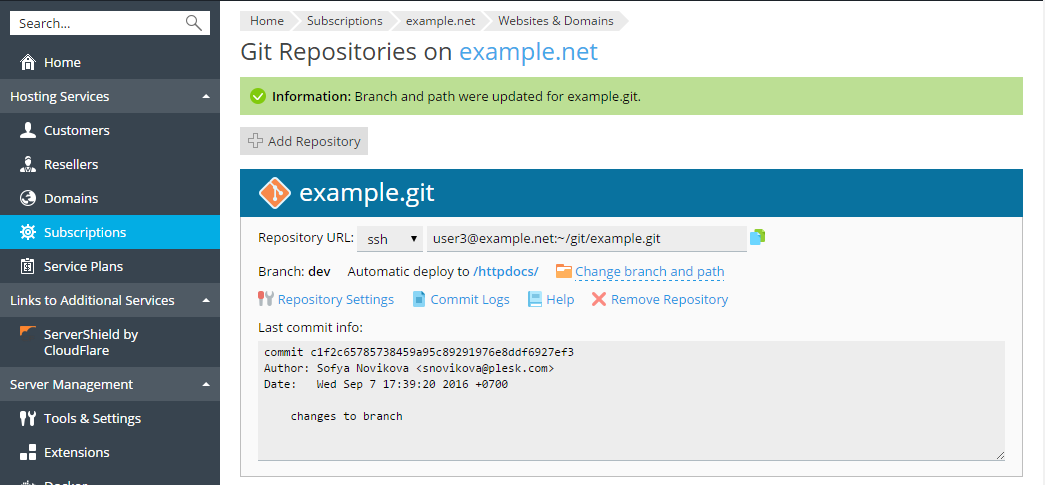
If you select a new branch and click OK, Plesk will display the new active branch.
Change the deployment path
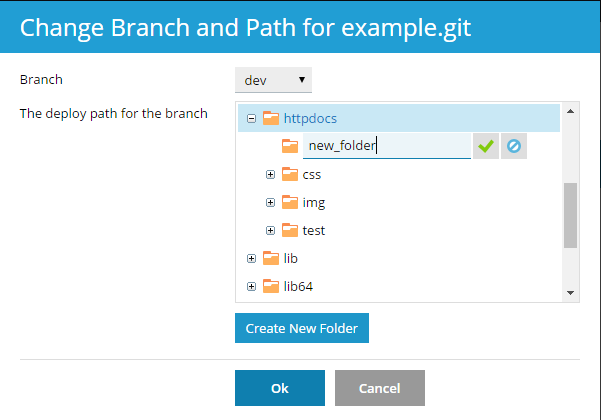
By default, the /httpdocs directory is used for publishing Git files on your website. If you want to change the deployment path, click the Change branch and path link, and in the opened window select the new directory. You can also create a new directory by clicking the Create New Folder button.
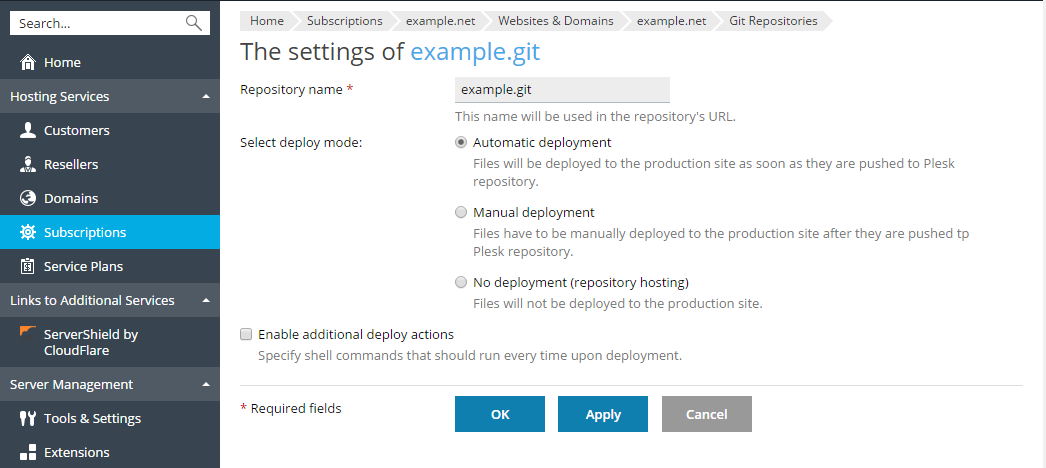
To select a deploy mode for your repository, click Repository Settings and select one of the options under Select deploy mode:
In most cases, file publishing is not enough to finish web site deployment. For example, if you are using frameworks like Ruby on Rails, you may need to run a data migration task after deployment with a command like this: bin/rails db:migrate.
Plesk gives you the ability to set a number of additional actions that will be performed each time the files are deployed to the web site.
Go to Websites & Domains > Git, click Repository Settings, select Enable additional deploy actions, and specify one or more shell commands that should be run every time this repository is deployed. Each command should be started on a new line.
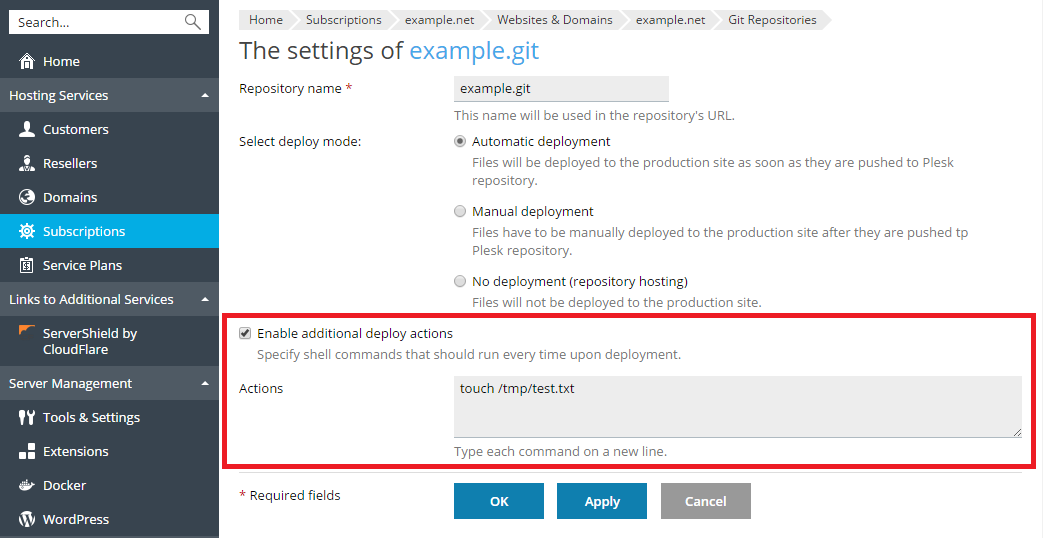
Note: If SSH is forbidden for the user on Linux, all the specified commands will run in a chrooted environment. The home directory of a subscription's system user is treated as the file system root for that subscription, and no executable files outside the chroot jail can be run. For example, if the path to your site is /var/www/vhosts/example.com/httpdocs, then, in a chrooted environment, the path will be ./httpdocs, so you will not be able to execute commands outside one level above the /httpdocs directory.
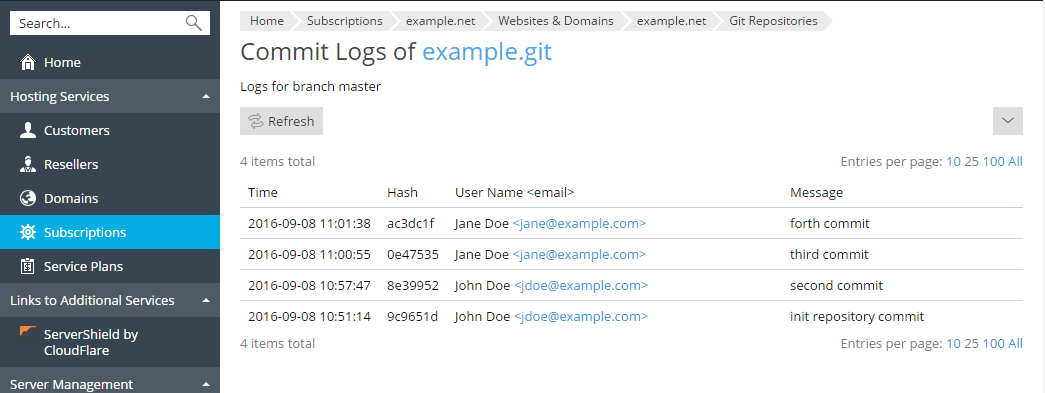
To view the whole commit history for the current branch, go to Websites&Domains > Git, and click the Commit Logs link. For each commit, the following information will be displayed: time, unique identifier, user name, and the commit message. Click Refresh to update the commit log.
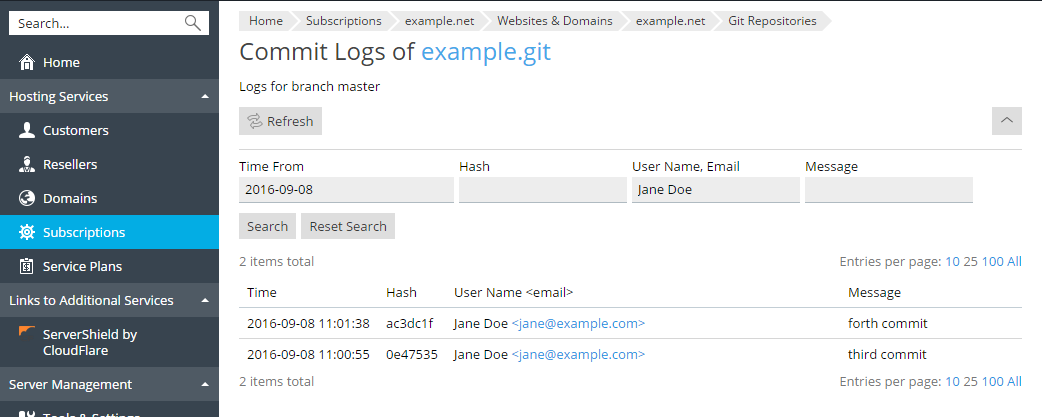
You can filter the commit logs by any parameter. For example, you can find all commits by a specific user starting from a particular date. Click the ![]() button, enter the search parameters, and click Search.
button, enter the search parameters, and click Search.
You can rename your repository at any moment. For example, if you have finished development, you may want to change the repository name from website-dev to website to avoid confusion. Go to Websites&Domains > Git, click Repository Settings, and enter a new name in the Repository name field.
Note that after renaming the repository, you should configure your local repository to work with the new repository URL, using the command:
git remote set-url origin [new URL]
For example, if you rename the repository from example to example1, run the command:
git remote set-url origin user1@example.com:~/repos/example1.git
If you want to remove the repository, click the Remove Repository link at Websites&Domains > Git. In this case, Plesk will remove just the repository; the target directory with the published data will remain as it is.